Comparing Preservative-Free Eye Drop Products in Canada & Looking Beyond
Michael Ng
DID YOU KNOW THAT DRY EYE IS SIGNIFICANTLY MORE PREVALENT & EXPERIENCE IN GREATER SEVERITY WITH AGE IN EYES OF ASIAN ETHNICITY THAN CAUCASIAN GROUPS? (See Study By Ji Soo Kim, Dr Michael Wang et al)
FIRST. Why is Preservative-Free Important?
We use eye drops daily for not only comfort, enhanced visual performance, and dry eye relief. Why not choose a drop that helps us most to be active at work, especially with increasing computer strain as we work from home.
Some preservatives can destroy the natural tear film AND cause damage to cell tissues, which makes it intolerable for long-term use.
Most older preservative-containing eye drops recommend disposal after only 30 days from opening. Meanwhile, preservative-free eye drops can last far longer 3, 6 and some up to 12 months from opening due to their nature of their bottle to keep drops clean by using separate compartments to prevent back-flow. This can significantly make your drops last longer while using something more safe for your eyes.
What about buffer systems?
The most common formulations of buffer systems used in eye drops are phosphate, citrate, borate, or Tris-HCL (Tris). Ideally, buffer systems help maintain the pH to help maintain the composition of the formulation to extend shelf life and mimic the natural tear film. The average physiological pH of lacrimal fluid is 7.4 (ranges from 6.5-7.6).
Phosphate buffers are the most widely used buffer since it has excellent capabilities at keeping pH levels neutral. In addition, as phosphate exists naturally on the surface of the eye, it is seen as a safe buffer. Selective case reports in rabbits with corneal abrasions noted that extremely high-levels of phosphate can bind to calcium released from damaged cells (epithelial keratopathy), which can form insoluble calcium deposits on the surface of the eye (corneal calcification). While other studies show risks associated with this is in humans is rather low without pre-existing corneal defects, this is particularly important to consider when using eye drops after corneal injury and post-laser surgery for healing. In a healthy eye, phosphate buffers are safe. Newer eye drops tend to use a citrate, borate, or Tris buffer to maintain a safe pH solution for the eyes; the latter being the least cytotoxic to cellular tissues and shows highest cell viability.
SECOND. The Goal?
This article is a non-bias analysis of preservative-free products available on the Canadian Market to help us better understand product ingredients, their active components, use AND shelf-life.
Learn The Basics of Dry Eye
Learn about Active Ingredients like Hyaluronic Acid
EYE DROP RANKING FOR HA %
%HA MAY NOT BE ENOUGH: Molecular weight, osmolarity
Discover Non-active Ingredients
Additive ingredients: what is Trehalose? HP GUAR?
Chart of ingredients of eye drops in Canada & Shelf-life
Future Dry Eye Products
Studies & Further Reading
“Preservative-free 無防腐劑
frei von Konservierungsstoffen 방부제 무료
sans conservateur 保存料フリー Không chất bảo quản konserveringsmiddel rotvarnarlaust
sin preservativos
ปราศจากสารกันบูด मुफ़्त परिरक्षक без консерванти
Säilöntäaineeton
bebas pengawet koruyucusuz konserveringsmiddel-fri kulondolozekile بدون مواد نگهدارنده χωρίς συντηρητικά
bez konserwantów preserveermiddel vry
senza conservanti”
The BASICS: What is Dry Eye?
Dry eye disease (DED) is a multi-factorial disease characterized by the loss of homeostasis of tear film by tear film instability, hyperosmolarity, and ocular surface inflammation. Artificial tears are the most common topical therapy for DED to supplement or replace our natural tear film.
Hyaluronic Acid (HA)
Why Sodium Hyaluronate / Hyaluronic Acid (HA)?
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a natural occurring glycosaminoglycan. Sodium hyaluronate is the salt form of HA, which is a more stable compound for topical application. It is commonly found in dry eye drops because it binds to water, prevents dehydration, and is highly biocompatible as it is naturally found in high concentrations in the eye. Studies show HA improves optical quality, promotes corneal epithelial wound healing by stimulating epithelial migration, and protects corneal epithelial damage.
HA vs CMC vs HPMC?
In vitro studies showed that HA preformed slightly better than carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) at water retention and protection of corneal epithelial cells. HA can not only retain water but also slowly release it over time.
WHICH IS BETTER? HA 0.1%, 0.18% or 0.3%?
In In Choen’s 2018 Study, all concentrations helped improve overall DED symptoms. The group with 0.3% HA showed the longest Tear Break Up Time (TBUT) over the 0.18% and 0.1% groups after 21 days. Tear-Break-Up-Time measures tear film instability by measuring the time it takes for the tears to first break up on the surface of the eye from the first complete blink. The study concludes that 0.3% HA is more effective than 0.18% and 0.1% in improving tear film stability, increasing conjunctival goblet cell density, and in protecting corneal epithelial cell damage. In Dorthea’s 2017 Study, 0.2% HA and 0.18% HA were shown to both efficacious and safe for the treatment of moderate to severe DED, with some parameters showing a non-significant trend favouring 0.2% HA over 0.18% HA.
CONCLUSION
~0.2% or less HA seems to be the sweet spot that provides both comfort while also not blur vision. While higher >0.2% HA appears to provide more dry eye relief for those who have more severe dry eye concerns but not afraid of some blur post-instillation. However, %HA may not be enough, scroll down to learn more.
which DROPS have Hyaluronate acid (HA)?
0.40% HA Ointment
0.30% HA Drops
I-DROP PUR GEL (HA + glycerin = 0.3% visoadaptive hyaluronan, phosphate buffer)
HYDRASENSE NIGHT THERAPY (citrate buffer)
0.2% HA Drops
HYLO GEL (high quality 0.2% HA, high molecular weight HA sourced from nature, citrate buffer, approved for Post Eye Surgery in Canada, best for sensitive eyes)
EVOLVE DAILY INTENSIVE (high quality 0.2% HA, borate buffer, approved in Canada Oct 29, 2020, status: to launch Feb 2021) - New article here
BIODROP MD PLUS - multi-dose (0.25% HA, 2% trehalose)
BIODROP MD - multi-dose (0.2% HA)
BIOTRUE - single dose (0.2% HA, phosphate buffer)
BIOTRUE - multi-dose (0.24% HA, phosphate buffer)
BAUCH & LOMB SOOTHE PF Dry Eye Therapy - single dose (0.24% HA, phosphate buffer)
0.2% HA+ Drops
EVOLVE INTENSIVE GEL (0.2% HA, Carbomer 980, Glycerol, buffer-free, approved in Canada Oct 29, 2020, status: to launch Feb 2021) - New article here
I-DROP MGD (HA + glycerin = 0.2% visoadaptive hyaluronan, + lipid layer enhancer, phosphate buffer)
0.18% HA Drops
I-DROP PUR (HA + glycerin = 0.18% visoadaptive hyaluronan, phosphate buffer)
0.15% HA Drops
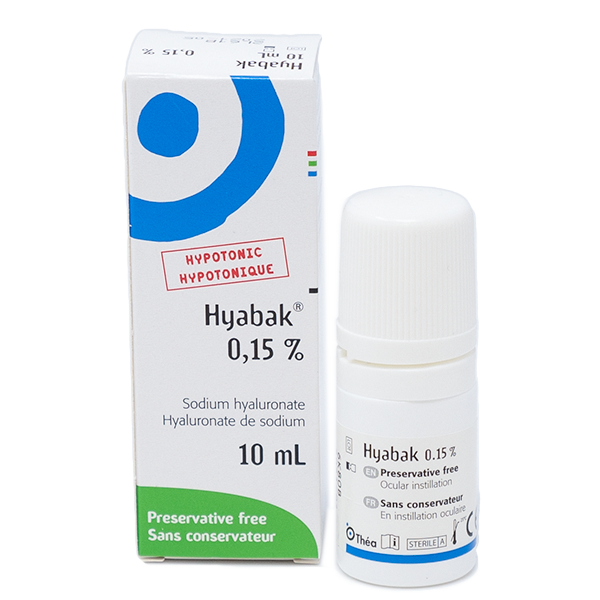
HYABAK (+Actinquinol: UVB protection, hypotonic, Tris Buffer, Made in France)
THEALOZ DUO (+Trehalose: Osmoprotectant, hypotonic, Tris Buffer, Made in France)
THEALOZ DUO GEL (+Trehalose: Osmoprotectant, hypotonic, Tris Buffer, Made in France)
0.10% HA Drops
HYLO (high quality HA, citrate buffer, approved for Post Eye Surgery in Canada)
0.03% HA Drops
HYLO FRESH (high quality HA + Euphrasia officinalis, borate buffer)
Contains HA at unknown%
SYSTANE ULTRA HYDRATION PRESERVATIVE-FREE SINGLE DOSE and MULTI-DOSE BOTTLES (Canadian Version only, HA + HP-GUAR)
BIODROP MD SPRAY - micro-emulsion spray bottle (HA + sea buckthorn seed oil)
For Allergies / Itchy red eyes: contains 2% ecotine
0.15% HA Drops
HYDRASENSE ALLERGIES (citrate buffer)
0.05% HA Drops
HYLO DUAL (high quality HA, citrate buffer, Made in Germany)
HA % alone may not be enough.
Because eye drops have a limited time in contact with the eye before it gets washed away, the time of direct contact is short for absorption. Reapplication is often needed and the number of drops to apply is difficult to recommend for severity of dry eye. Higher viscosity drops tend to allow for higher bioavailability of the drug. The drop size, its composition and molecular weight will also need to be considered.
Molecular Weight: Long vs Short chain HA
The concentration of HA does not always reflect the molecular weight. It is possible to have a high molecular weight HA at a lower concentration in a formulation, which can outperform one with a higher concentration of HA. For example, HYLO (high-MW HA) vs HYABAK & HYDRASENSE (low-MW HA). High-quality HA depends on the molecular weight, which is related to the length of the chain of each molecule.
High molecular weight HA will be more cohesive since it will take more time to breakdown than low molecular weight HA. It promotes adult regenerative healing. It can sit on the ocular surface longer to draw moisture and continually hydrate the cornea. Low-quality HA is more dispersive due to its light weight, which can bind with other molecules and cascade an inflammatory response. In the future, cross-linked HA may play a role to being more beneficial than non-cross-linked HA (i.e. AEON PROTECT PLUS).
High-molecular weight HA (>1000 kDa)
OSMOLARITY PLAYS A FACTOR
Since Hyperosmolarity contributes to DED. Hypotonic solutions have been shown to offer greater improvements than isotonic solutions.
A 2008 study showed that by reducing the osmolarity of tear film, the hypotonic solution not only improves the characteristics of tear film and the vitality of the epithelial cells of the cornea and conjunctiva but also proves to be effective in reducing dry eye symptoms.
It compared preservative-free 0.4% HA drops in dry eye patients at 300 mOsm/L and another 150 mOsm/L. At the end of the study, 60.7% of the patients declared that they preferred hypotonic solution and only 10.7% preferred isotonic solution; the remaining 28.6% did not notice any difference between the 2 treatments.
Hyabak, Theolaz Duo and Theolaz Duo Gel eye drops are all hypotonic.
CANDORVISION eye drops around 280 mOsm/L, hypotonic.
What about The Other Ingredients in Eye Drops?
Table information extrapolated from Artificial Tears Primer (2016). See link below to read more.
What’s the difference between GLYCEROL vs GLYCERIN?
Actually, both names are for the same molecule; however, Glyercin is the commercial name of Glycerol, which is not pure and contains at most 95% of glycerol. Evolve’s Intensive Gel uses a pure glycerol and is also buffer-free. In comparison, I-DROP PUR and PUR GEL uses glycerin.
What about Trehalose?
Trehalose (TH) is a natural disacchiride that is both a bioprotectant and osmoprotectant. On the eye, it protects corneal and conjunctival cells from desiccation (cell death in absence of water) by:
The immobilization theory: Trehalose encases & protects proteins
The preferential exclusion theory: Trehalose keeps water out of proteins by becoming more compact
The water replacement theory: Trehalose replaces water, increasing its stability
Osmoprotectants protect cells against hyperosmolarity. In Schmidl’s 2015 study, trehalose can increase tear film thickness up to 240 minutes vs drops without trehalose.
The TFOS International Dry Eye Workshop II (DEWS II) recognizes trehalose as an effective ingredient with HA in moderate to severe dry eye.
HA + Trehalose Drops
Trehalose + HA vs. Hyaluronic Acid ALONE?
In a 2009 study comparing preservative-free trehalose 3%, hyaluronic acid 0.15%, carbomer 0.25% (TH HA, Thealoz Duo Gel) vs hyaluronic acid 0.3% gel drops (HA). The results showed both groups preformed well for up to 120 minutes for Tear meniscus height (TMH) and tear meniscus depth (TMD). TH HA (Thealoz Duo Gel) mean comfort duration was 115 min and 0.3% HA mean comfort duration was 148 min. Tear osmolarity, Schirmer I test, and TBUT were similar at 240 mins for both groups.
Conclusion: The study concluded that 0.3% HA remains on the ocular surface for longer than TH-HA by about 33 minutes. The longer time seemed to correlated to patient comfort.
WHAT IS HP-GUAR?
HP-GUAR acts as a viscous gel, which is derived from natural guar galactomannan, a water-soluble polysaccharide which has been treated with propylene oxide. HP-GUAR molecules have a high molecular weight (1,000–5,000 kDa), which accounts for the viscous nature of the gel.
HP‑GUAR and HA, appears to adhere to the muco‑aqueous layer of the tear film as well as the cells of the epithelium. An individual 2015 study showed that HA + HP-GUAR had about twice the cell viability after treatment than HA / HP-GUAR alone. The amount of HA concentration was not stated. The protective effect remained on the surface of the eye after 4 hours even after wash.
HP-GUAR and HA can be found in Systane Ultra Hydration PF drops in Canada.
SUMMARY: COMPARING PRESERVATIVE-FREE EYE DROPS IN CANADA CHART
Upcoming Novel Ingredients: Two Mucin Secretagogues (Diquafosol vs. Rebamipide) - not available & approved in Canada
Figure 1- created by Shizuka Koh. Study link below.
1) Diquafosol sodium 3%
Diquafosol sodium improves tear film stability by increasing tear volume and mucin secretion. This may inhibit tear hyperosmolarity. More specifically, it stimulates water and mucin secretion by acting on P2Y2 receptors on the conjunctival epithelium and goblet cells and meibomian glands.
DIQUAS
Diquas became available in December 2010 in asian countries including Korea, Vietnam, Thailand, and Japan (2012).
USE: Apply 6 times daily regardless of severity of dry eye
Long-term use with Diquas reduces higher-order aberrations (HOAs), increase tear film stability, reduces tear break up time, and reduces corneal epithelial damage better than 0.1% hyaluronate after 4 weeks of use.
Additive effect
There is an additive effect of diquafosol sodium 3% with hyaluronate 0.1%/0.3% showed greater improvement than just hyaluronate therapy alone in dry eye patients. Although more studies need to be conducted.
2) Rebamipide 2%
Rebemipide improves tear film stability by improving epithelial condition. More specifically, it acts by increasing epithelial differentiation.
Rebemipide has also found to have anti-inflammatory effects and promotes epithelial healing in animal models, which may reduce epithelial damage, and provide tear stability.
MUCOSTA ophthalmic suspension
Launched in Japan 2012
USE: Apply 4x daily
Which therapy is more effective?
We know that both diquafosol sodium 3% and rebamipide 2% upregulate MUC16, which increases tear stability. Diquafosol sodium improves tear film stability by increasing tear volume and mucin secretion, while Rebemipide improves tear film stability by improving epithelial condition and may have anti-inflammatory effects to promote epithelial healing. Overall, more clinical studies need to be conducted to clarify its long-term effects and use case.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS:
STUDIES / ADDITIONAL READING
Corneal Calcification (2006): https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1856937/
Comparison of 0.1%, 0.18%, and 0.3% Hyaluronic Acid Eye Drops in the Treatment of Dry Eye (2018): https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/jop.2018.0032
Comparison of HA & CMC (2018): https://www.healio.com/ophthalmology/cornea-external-disease/news/online/%7Beac8107e-2636-45fc-b2bb-295b9b2471ae%7D/two-dry-eye-drop-formulations-compared
Trehalose: A novel treatment for dry eye (2018): https://www.healio.com/ophthalmology/cornea-external-disease/news/print/ocular-surgery-news/%7B6d1f0d15-4321-487b-8aa8-56648bdec2d2%7D/trehalose-a-novel-treatment-for-dry-eye
Artificial Tears Primer (2016): https://webeye.ophth.uiowa.edu/eyeforum/tutorials/Artificial-Tears.htm
Effects of Preservative-Free 3% Diquafosol in Patients with Pre-existing Dry Eye Disease After Cataract Surgery (2019): https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-49159-0
Diquas by Santen Osaka Japan: https://www.santen.com/en/therapeutic-areas/asia/dryeye/diquas/
Medical Treatment of Dry Eye in Japan (2018): https://iovs.arvojournals.org/article.aspx?articleid=2717221
Clinical utility of 3% diquafosol ophthalmic solution in treatment of dry eye (2015): https://www.researchgate.net/publication/277602357_Clinical_utility_of_3_diquafosol_ophthalmic_solution_in_the_treatment_of_dry_eyes
Rebamipide ophthalmic suspension for the treatment of dry eye syndrome: a critical appraisal (2014): https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4051796/
Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis with Ectoine Containing Nasal Spray and Eye Drops (2014): https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ja/2014/176597/#conclusions
Comparison of 0.2% and 0.18% hyaluronante eye drops in patients with moderate to severe dry eye with keratitis or keratoconjunctivitis (2017): https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5388258/
Dry Eye in Vitamin D deficiency (2015): https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/1756-185X.12727
Optimization of hyaluronan-based eye drop formulations (2016): https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0144861716309043
Kim JS, Wang MT, Craig JP. Exploring the Asian ethnic predisposition to dry eye disease in a paediatric population. Ocul Surf. 2018
Craig JP, Wang MT, Kim D, Lee JM. Exploring the Predisposition of the Asian Eye to Development of Dry Eye. Ocul Surf. 2016 Jul;14(3):385-92.
Comparison Study of TH HA drops vs 0.3% HA drops (2019): https://www.contactlensjournal.com/article/S1367-0484(19)30218-8/fulltext?dgcid=raven_jbs_etoc_email
Effect of Hypotonic 0.4% HA drops in Dry Eye Patients (2008): https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19034126/
Sodium Hyaluronate of different osmolarity for treatment of dry eye in Sjorgen’s Syndrome patients (2012): https://www.researchgate.net/publication/11242163_Sodium_hyaluronate_eye_drops_of_different_osmolarity_for_the_treatment_of_dry_eye_in_Sjogren's_syndrome_patients
HA: No Laughing Matter (2018): https://www.reviewofoptometry.com/article/ha-no-laughing-matter
Physiochemical Properties of Hyaluronic Acid-Based Lubricant Drops (2019): https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6827422/
Hyaluronic Acid Yes Size Does Matter (2015): http://barefacedtruth.com/2015/03/31/hyaluronic-acid-yes-size-does-matter/
Indications for Ophthalmic Formulations: Ocular Buffers Showed Varied Cytotoxic Impact (2017): https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5421463/
Biological Production of Hyaluronic Acid: Mini Review (2016): https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4754297/
Effects of a Hyaluronic Acid/Hydroxypropyl Guar Artificial Tear Solution on Protection, Recovery, and Lubricity in Models of Corneal Epithelium (2015): https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26067908/
Impact of polyethylene glycol 400/propylene glycol/hydroxypropyl-guar and 0.1% sodium hyaluronate on postoperative discomfort following cataract extraction surgery: a comparative study (2017): https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5424421/
Tear osmolarity changes after use of hydroxypropyl-guar-based lubricating eye drops (2017): https://www.dovepress.com/tear-osmolarity-changes-after-use-of-hydroxypropyl-guar-based-lubricat-peer-reviewed-fulltext-article-OPTH#:~:text=Hydroxypropyl%2Dguar%20(HP%2Dguar)%20is%20an%20agent%20found,been%20treated%20with%20propylene%20oxide.
Disclosures
As part of Amazon’s Association Program, we would like to disclose that we use Affiliated Amazon links to not only help you find what you’re looking for, but these product links allow us to generate revenue to support writing great articles for this site.